IPSec Tunnels Configuration
Companies can host their services and applications within internal networks (Intranet) that do not expose endpoints to the internet. In this case, if an IAM provider needs to provision or synchronize with the applications, they cannot do so via standard public access.
To address this, IPSec (short for Internet Protocol Security) provides a secure and encrypted tunnel between two networks. By encrypting the data at the source and decrypting it at the destination, IPSec allows systems on each side to exchange information securely.
How Memority Uses IPSec
Memority uses IPSec when a client requires on-premise provisioning for an application hosted on their Intranet. In these cases, the application is not accessible from the internet, so Memority cannot perform account synchronization or API calls through a standard public connection.
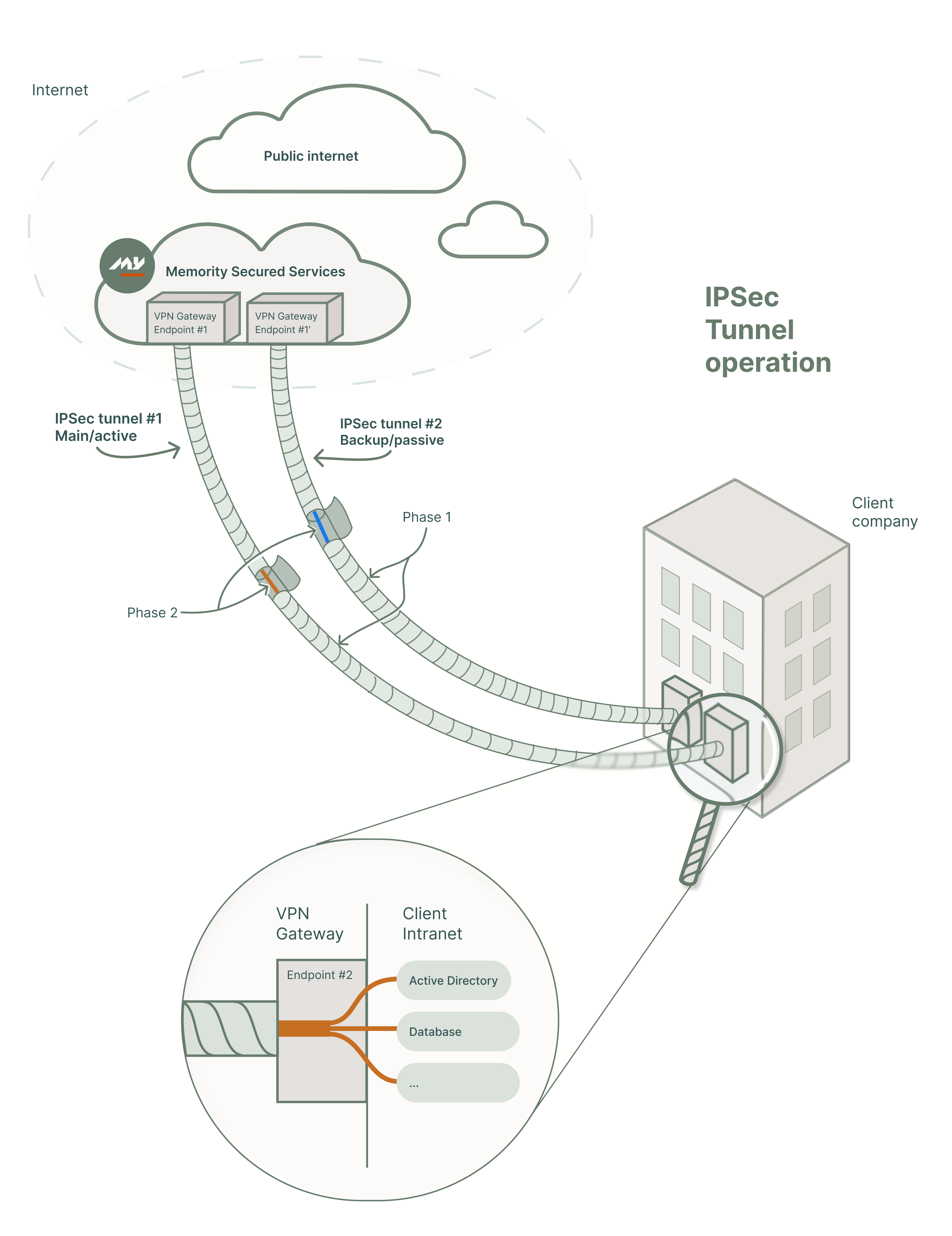
To establish secure access, Memority sets up an IPSec tunnel between its infrastructure and the client’s Intranet. This tunnel provides a safe path for provisioning operations while maintaining strict isolation from the public internet.
In most deployments, Memority sets up two tunnels:
Main IPSec tunnel
Handles the primary communication used for synchronization and other remote tasks.
Backup IPSec tunnel
Activates if the main tunnel becomes unavailable, to guarantee service continuity.
Each tunnel links specific endpoints and limits the access to only what is necessary for provisioning.
Understanding IPSec Phases
Memority uses IPSec to create a VPN tunnel between Memority and the client’s Intranet. This tunnel provides a secure, encrypted path for remote application management.
The IPSec VPN tunnel follows a two-phase structure, consisting of Phase 1 and Phase 2.
You can think of these phases as nested layers where one tunnel wraps around the other.
Each phase uses its own encryption key.
Phase 1: The Outer Tunnel
Phase 1 forms the secure outer shell of the connection. It established an encrypted connection between the IPSec termination points on both sides (typically firewalls or network gateways).
This tunnel connects a public IP from the client to a public IP from Memority.
This phase establishes the trust channel. If Phase 1 drops, no communication is possible.
Phase 2: The Inner Tunnel
Phase 2 operates inside the tunnel established by Phase 1. It defines which private IP ranges can communicate across the connection. This is where routing happens, for example, between Memority’s synchronization service and the client’s internal ERP or Active Directory applications.
Common internal IP ranges include:
10.x.x.x (Class A)
192.168.x.x (Class B)
172.16.x.x – 172.31.x.x (Class C)
Memority and the client each assign a local IP to their respective services. The IPSec configuration links those subnets to enable secure communication.
You can also configure multiple Phase 2 tunnels under a single Phase 1 to separate environments or application zones. This configuration can apply if the client has two sub-networks, for example.
Memority IPSec Requirements
Before setting up IPSec tunnels for on-premise provisioning, the client and Memority need to align on technical requirements.
IPSec Configuration
ID | Requirements | Applies to |
|---|---|---|
IPS001 | Encryption algorithm must be one of the following:
| Phase 1 and Phase 2 |
IPS002 | Hash algorithm must be one of the following:
| Phase 1 and Phase 2 |
IPS003 | Diffie-Hellman group must be one of the following:
| Phase 1 and Phase 2 |
IPS006 | Memority team will generate the PSK key with respect to the following requirements
| Phase 1 |
IPS007 | IKE must be version 2 |
Network Configuration
ID | Requirements | Description |
|---|---|---|
NET001 | Remote network (client) must be valid | Use the first address of the IP range (e.g., |
NET004 | Use the smallest possible CIDR range | Prefer CIDR |
DNS Configuration
ID | Requirements | Description |
|---|---|---|
DNS001 | All FQDNs must be private | DNS names must not resolve publicly and should remain internal-only |
DNS002 | Provide all FQDNs with both hostname and domain | Example: |
DNS003 | Associate each FQDN with a single IP in CIDR/32 format | Example: |
DNS004 | Use consistent domain naming within the same Phase 2 configuration | Example: |
High Availability (HA) Configuration
ID | Requirements | Description |
|---|---|---|
HA001 | Configure one Phase 1 tunnel per Memority environment hosting the client tenant | This avoids conflicts between environments such as production and staging |
HA002 | Configure a backup Phase 1 tunnel for DRP | Set up one active and one inactive tunnel for disaster recovery planning |
Monitoring Configuration
ID | Requirements | Description |
|---|---|---|
MON001 | Configure monitoring on the client side | Memority monitors IPSec Phase 1 and Phase 2, without on-call configuration |
MON002 | Notify Memority before decommissioning any target | This prevents incidents caused by unexpected changes |
Setup Procedure
Please contact Memority support to validate your configuration and set up the tunnels.
