Attributes
Definition
Attributes Definition are entities that define the properties of Objects types. When starting to configure a Memority environment, you need to create Attributes definition to be able to link them to Object Types (this was referred as “attribute bindings” previously).
By Default, When the Memority environment is created, we propose some standard attributes definition, that can be customized according to the needs. Therefore if the existing attributes definition are sufficient to configure the client's data model, it is not mandatory to create new ones.
Attributes properties are used to describe the core characteristics of the Attributes.
By default, all configured Attributes are available for use on all Object Types, except if the Attributes definition explicitly define the Object Kind on which it can be apply to.
In the same way that “Identity Types” are not identities, “Attribute Definitions” are not attributes “values”. They represent a configuration that describe the type of value expected (string, boolean, number etc.) and the rules that will be applied (lowercase, unicity etc.). When we talk about the attribute “firstName”, we mean its definition. When we talk about an identity’s firstName, we mean its value (ex: “John”).
There are three types of Attributes:
Built-in: these Attributes are predefined, reserved by the system and their values can be modified (except: kind, id, entityId, type).
Meta: these Attributes are positioned by the system, they cannot be modified by users. Those are read-only Attributes.
Configurable: these Attributes are created by the user.
Configuration
You can access the Attribute configuration :
by clicking on "Data Model" → "Attributes"
by clicking on "System" → "Configurations" and perform an import/export.
Properties
Parameters name | Type | Mandatory | Description | Values (default value in bold) | Modifiable after creation |
identifier |
| YES | The unique id of each Attribute that will be reused in the configuration (Features etc…). It is case sensitive and no special characters (except - or _) are allowed. | - | NO |
name |
| YES | The name of the Attribute. Specifying the name first allows you to define automatically the identifier. | - | YES |
objectKind |
| NO | Used to dedicate an Attribute to an Object Kind. If no value entered, the attribute can be used on all Object Kind. | Identity, Resource, Organization, Role or Role publication, SOD Rule | NO |
confidentiality |
| NO | The purpose of confidentiality is to hide or not the Attribute. Allows user to see the value of the Attribute if it corresponds to the level defined. You must define a right on a Feature with a confidentiality level. If the confidentiality is set to 1, the user will be able to see Attributes which are confidentiality level 0 and 1. | 0, 1 or 2 | YES |
description |
| NO | The purpose of the Attribute. | - | YES |
virtual |
| NO | Used to indicate if the Attribute is a virtual or not. A virtual Attribute is resolved (according to the resolve rule) each time it is accessed on the Object to which it is attached. This property can be used to put online help on a built-in Attribute. | ON or OFF | NO |
highPriority |
| NO | Prioritization level for changing the value of an Attribute. If an Attribute is configured with a "high priority", when this Attribute is modified on an IDM object (either via a "create" or a "patch" operation), the event message triggered by this modification is generated with a "high priority" so that it is processed accordingly by other services listening on such an event messages. For example, Synchronization service, upon the reception of such a "high priority" message, will trigger as soon as possible provisioning operations for the IDM object who is the subject of the message. This is namely useful to quickly propagate an IDM password change to a provisioned LDAP directory, so that the user whose password was changed can immediately authenticate to this LDAP directory using the new password. The built-in IDM "password" attribute has indeed a high priority. Some built-in Attributes (as password, enabled, ...) have this priority to high. | ON or OFF | YES |
valueType |
| NO | The type of the Attribute. | String, Date, Date & Time, Integer Number, Decimal Number, Binary, Boolean, Identity, Resource, Organization Role or Role publication | NO |
minLength |
| NO | Minimum length of the string value type. | - | YES |
maxLenght |
| NO | Maximum length of the string value type. Beware if more than 255 characters are expected in the string, specify the max value | - | YES |
choicesRule |
| NO | Used to build lists of choices (possible values to be chosen for an attribute). This rule serves as a validation rule. | Reference Table or Groovy Script | YES |
scope |
| NO | A Scope can limit the displayed results. For example, you can define that "manager" Attribute must be:
In this case, the search results will only display the manager completing these criteria. Note that only searchable Attributes can be used in a Scope. | - | YES |
multiValued |
| NO | Indicates if the Attribute can have several values (companies, supervisors ...) Not applicable for boolean value type. | ON or OFF | NO |
searchCriterion |
| NO | Indicates if the Attribute can be used in search requests (as search criteria). Not applicable for binary value type and virtual Attribute. | ON or OFF | YES |
internalAttributeId | - | NO | This property is mapped with the physical Attribute of the database. Recommendation : Choose automatic in order to let the application choose the internal Attribute id. The selection will be done in chronological order. Note that an internal Attribute id is unique throughout the application except if the Attribute is dedicated to one specific kind. | Automatic | NO |
readOnly |
| NO | Indicates if the Attribute can only be displayed and not modified. Not applicable for binary value type. | ON or OFF | NO |
| NO | Used to set the value of the Attribute at the creation of the Object only. If a compute rule is configured on the same Attribute, the initialization rule have priority. | - | YES | |
| NO | Used to calculate (every time) the value (before storing it in the database) of the Attribute at each modification of the Object (even if the modification is not on this Attribute). For example: if the Object is an external, then the badge is not allowed. Beware that compute rule doesn’t override the initialization rule (if any). | - | YES | |
| NO | Used to modify the entered value of the Attribute before storing it in the database. In this case, even if the value is not entered in uppercase, the value will be saved as defined in the rule. Only for string value type. | - | YES | |
| YES if virtual is set to ON | Same definition as compute rule but for virtual Attributes. Only the resolve rule is mandatory for virtual Attributes. | - | YES | |
| NO | Used to validate the value of the Attribute (whether it's allowed or not). | - | YES | |
secret |
| NO | Indicates if the Attribute is a secret and will not be displayed in clear text. Not applicable for binary value type. | ON or OFF | NO |
encrypted |
| NO | Indicates that the Attribute value is encrypted when stored. Not applicable for boolean, decimal number, integer number, date and date & time value types | ON or OFF | NO |
immutable |
| NO | Indicates if the Attribute value cannot be changed once created. | ON or OFF | NO |
system |
| NO | Indicates if the Attribute is managed by system tasks only. | ON or OFF | NO |
| NO | Used to define if the value is unique (at the creation of the Object). Only if search criterion = ON and value type = String. Characteristics:
| - | YES |
Built-in Properties
Built-in properties names are reserved keywords; they cannot be used to define a configurable Attribute.
Common to all Object Types
Name | Type | Mandatory | Description | Values | Searchable |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
kind |
| YES | The kind of the Object. | Identity, Organization, Resource, Role, Role publication | YES |
id |
| YES | The unique identifier of an Object Type that will be reused in the configuration (Features etc...) | - | YES |
entityId |
| YES | The identifier key (not necessarily unique) and which allows to link siblings. In other words, siblings have the same entityId. Objects having the same entity_id share the same "structural" Attributes. | - | YES |
type |
| YES | Type of an Object Kind, such as "employee" or "collaborator". | - | YES |
status |
| YES | The status of the Object. | Draft, Normal, Delete | YES |
enabled |
| YES | Indicate if the Object is enabled or disabled. Linked with the following attributes: objectActivationJob, enabledfrom, enabledUntil, disabledAt, activationMode. | true, false | YES |
enabledFrom |
| NO | The date from which the object is considered enabled. | - | YES |
enabledUntil |
| NO | The date from which the object is considered disabled. | - | YES |
flags |
| NO | List of flags on the user. Flags can be used to trigger action on specific population depending on context. | F00 to F15 | YES |
reservedFlags |
| NO | List of reservedFlags on the user. It can provide information on the last operation performed on the identity. Contrary to flags attribute they can not be set by end user, they are only set by system. | BYPASS_DEDUP, BYPASS_INTEGRITY, BYPASS_UNICITY, BYPASS_VALIDATION, PASSWORD_EXPIRED, PASSWORD_GRACE | YES |
Specific to Identities
Specific to Organizations
Specific to Resources
Specific to Roles
Specific to Roles Publication
Specific to SOD Rules
Meta properties
Meta properties are reserved keywords; they cannot be used to define a configurable Attribute
Common to all Object Types
Name | Type | Description | Searchable |
|---|---|---|---|
createdAt |
| The object creation date. | YES |
disabledAt |
| Date at which "enabled" was set to false. | YES |
deletedAt |
| Date at which "status" was set to delete. | YES |
updatedAt |
| The object last update date. | YES |
activationModes |
| Mode that can be used when activating/deactivating an Object. These are to be used, typically, in scripts. By default : AUTO or Admin (can be updated using setting) | YES |
Specific to Identities
Specific to Organizations
Specific to Roles
Rules
A rule can be entered as a groovy script or, for some of them, as a regular expression.
Rules apply when creating/updating a managed Object instance (through either the user portal functions or the upstream provisioning).
Note that some rules are not compatible with each other:
A normalize rule can only be combined with an initialization rule and/or a validation rule.
A choices rule may only be combined with an initialization rule.
A resolve rule can only be combined with an initialization rule and/or a compute rule and/or a validation rule.
The following Rules are dedicated to the Attributes definition, all Rules are detailed in a dedicated page.
Resolve rules
Resolve rules are used to calculate the value each time the object (only if the attribute is virtual) is modified or read. At each modification, the data is not recorded in database.
It is mandatory for virtual Attributes.
When configuring resolve rules there are two possibilities:
How | Example | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | By Random Identifier Generator: | Not relevant on a resolve rule. |
| 2 | By groovy script:Used to combine several Attributes' values for another Attribute. |
CODE
In this case, the value of the "level" attribute is resolved according to the status. |
Unicity rules
Unicity rules are used to define if the value of an Attribute is unique. Unicity rules can be global or limited to a specific Object Type.
When configuring an unicity rule, there are several properties to configure :
Limited to object type (ON or OFF) : When set to ON, the value will be unique whatever the Object Type (license plate).
Check on update (ON or OFF) : When set to ON, with each modification of the value of the Attribute, there will be a complete check before recording in database.
Search operator : Allows you to choose the operator to check the uniqueness (see the section on search Features which describes the types of operator). The most common is to use “equals” so that the rule checks that the data is not equal to itself.
Normalize: (The normalization rule applies before the unicity rule).
Capitalization : the value of the first letter will be in uppercase and the rest in lowercase. The "Full capitalization" checkbox allows the rule to be applied to the entire value chain.
Lowercase : the string value is stored in lowercase.
Uppercase : the string value is stored in uppercase.
Script : allows you to create a groovy script in order to configure more complex rule.
Attributes Inheritance
Principles of Attribute Inheritance
Applying Attribute inheritance means:
when creating a new child Organization, copy inherited Attribute values from the direct parent
when patching an inherited Attribute on a parent Organization, propagate changes to all child Organizations
when attempting to patch an inherited Attribute on a child Organization, throw a validation error
Attribute inheritance when creating a child Organization:
If an Attribute is inherited but the direct parent does not have this Attribute, then the child does not have it either.
An Attribute inherited from a child Organization will take the value of the parent’s attribute. If the Attribute does not exist on the parent, no value will be returned. There is a configuration inconsistency.
Validation error on attempt to:
create a non-root Organization by explicitly providing inherited Attribute values
create a non-root Organization whose parent type is not among the authorized parent Organization Types
Attribute inheritance when creating a parent Organization:
Propagating inherited Attribute changes from a root Organization to its children is similar to propagating structural Attribute changes to siblings; validation shall namely be disabled in both cases.
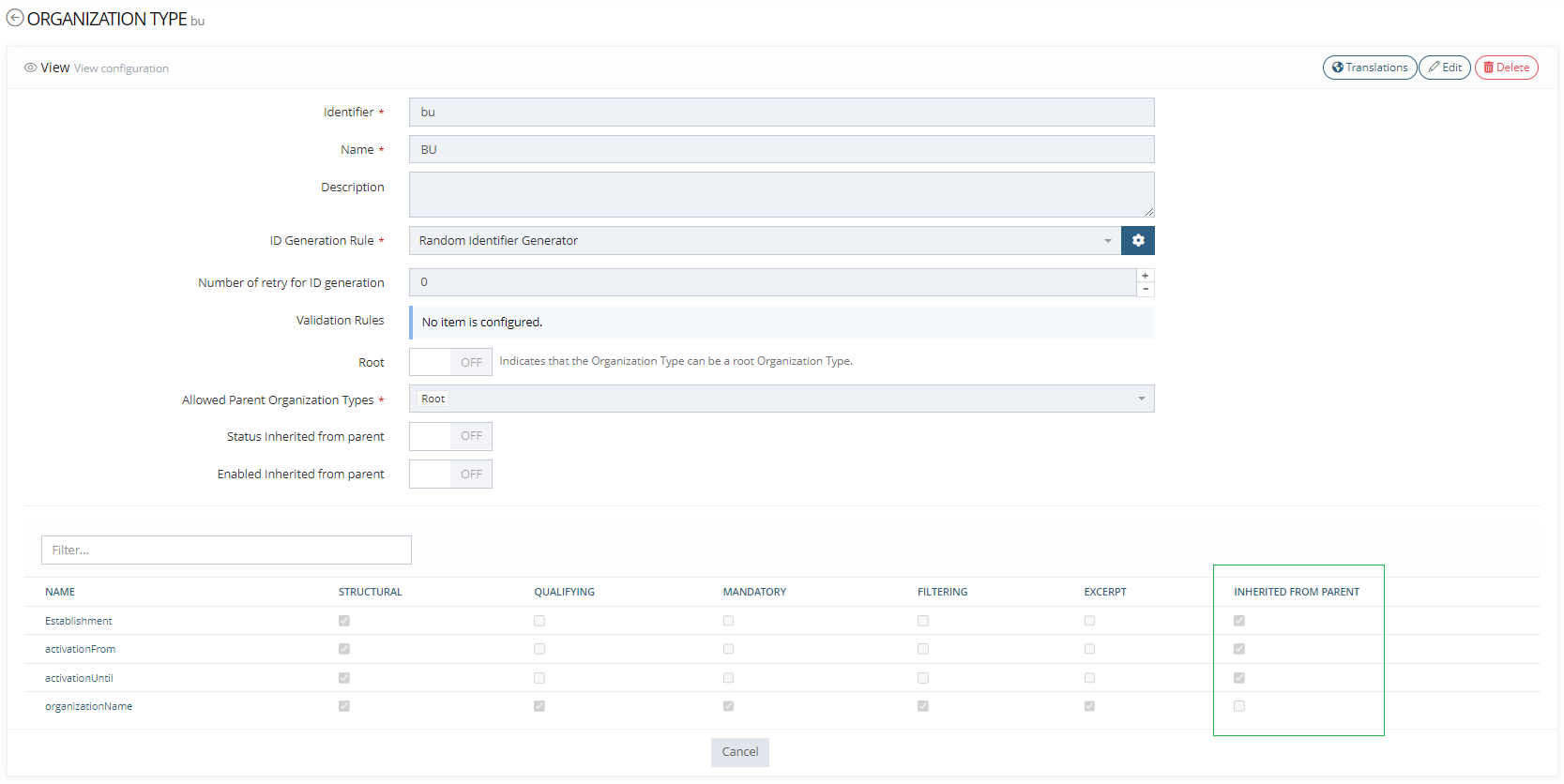
Configuring Attribute Inheritance
Attribute inheritance can be configured at any level of the Organization tree (not just at the root level).
When configuring an Attribute as inherited on an OrganizationType, a validation error is thrown if the Attribute is either computed/resolved/virtual/secret/encrypted.
Read Next
- Attribute Editor
Editor attributes are used to define the style to be used in read and write mode for an attribute.
- Features
Design screens and business features to manage objects.
- Object Types
An Object Type allows to define the types of Object that will be managed in the Memority Portal application and used in Features, rules etc...
